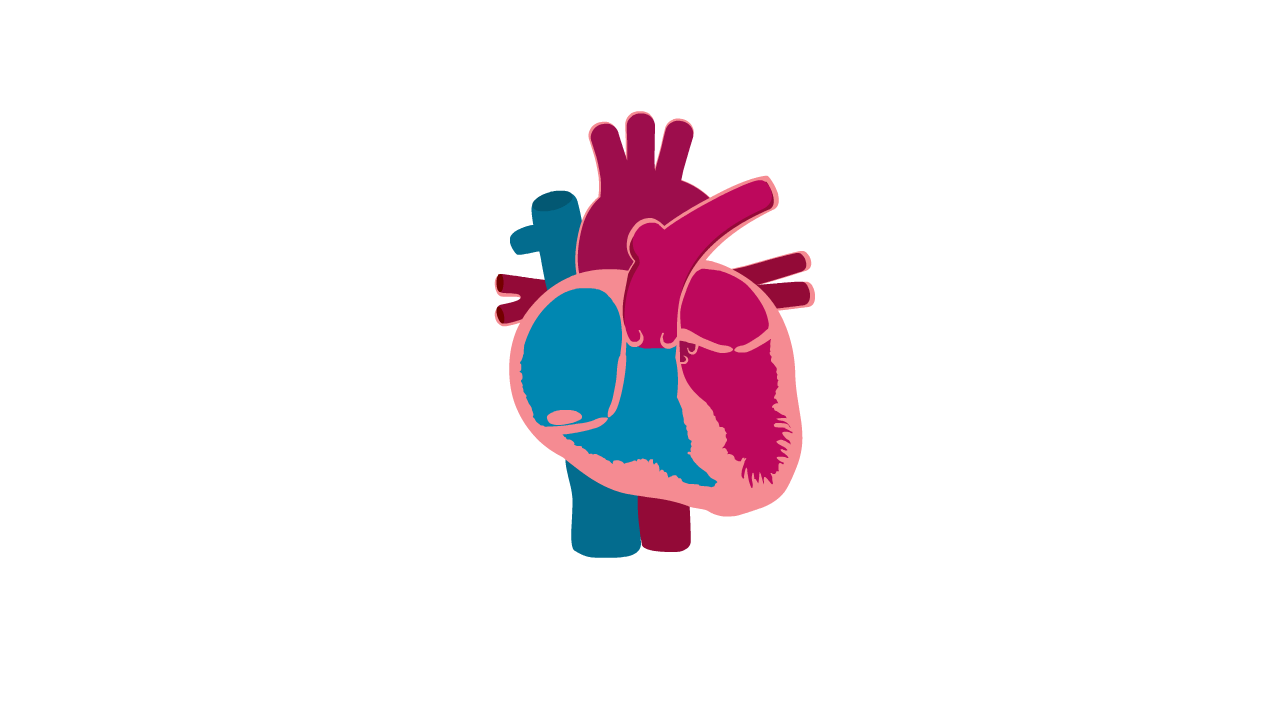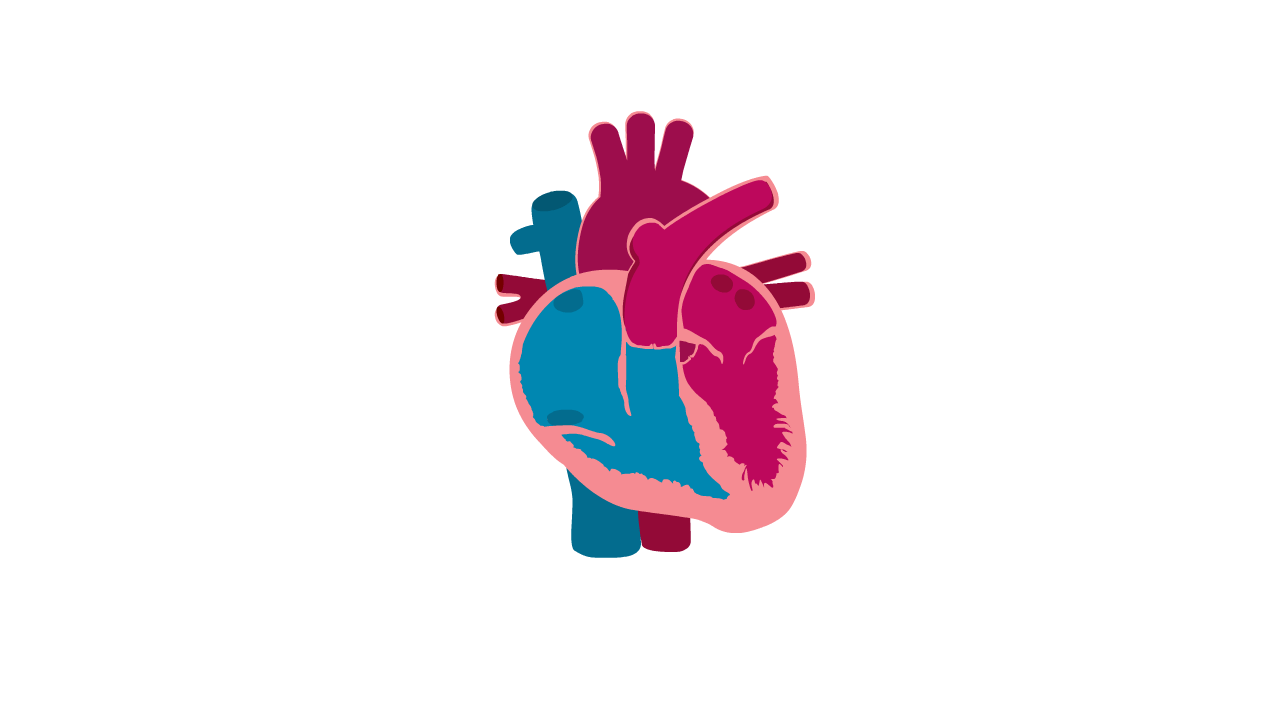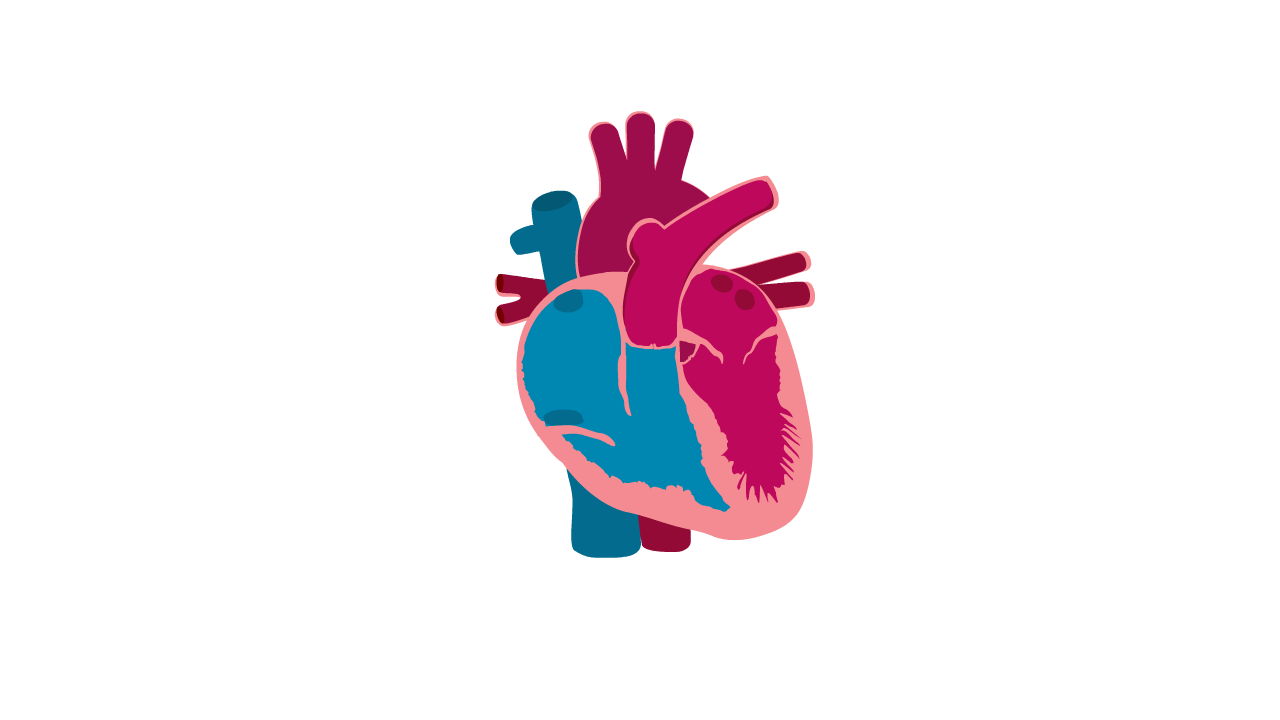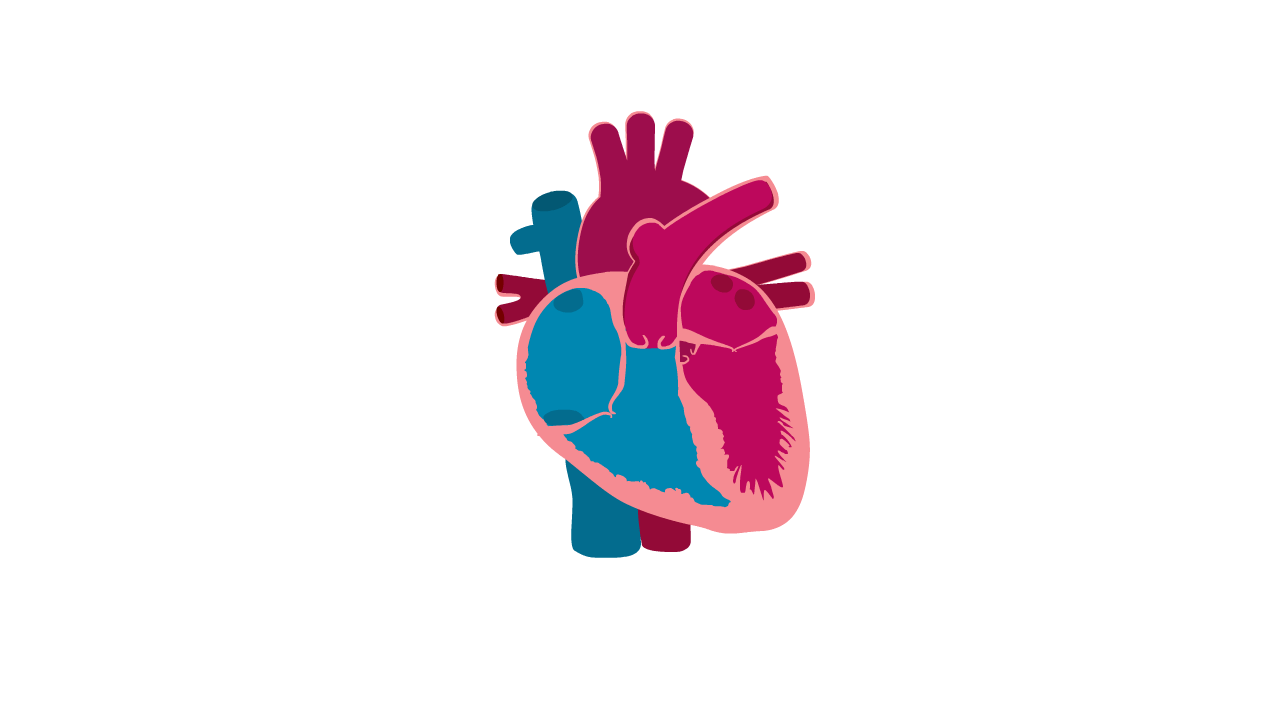
What is Left Ventricular Non-Compaction Cardiomyopathy (LVNC)?
- LVNC is a condition where the muscular wall of the heart appears 'spongy'.
- It can affect the heart's ability to work efficiently as a pump, and affect the electrical signalling of the heart.
- Although it cannot be cured, treatment is available for people who experience symptoms.
Not everyone with LVNC has symptoms (some people never have any symptoms). Symptoms vary from one person to another depending on the amount and position of the non-compaction, and they are not specific to LVNC (they can happen with other types of cardiomyopathy, and other conditions, which can make diagnosis difficult). Symptoms of LVNC can include:
- breathlessness
- fatigue (extreme tiredness)
- feeling dizzy or light-headed
If someone has a family member with cardiomyopathy or LVNC, or they have symptoms that suggest they may have a heart condition, they may be referred for various tests. This may include the following:
- Medical history and family tree - to look at symptoms and whether other family members have this condition (which can be genetic).
- Physical exam - to see what physical symptoms, if any, are experienced.
- ECG (electrocardiogram) - to look at electrical activity in the heart and see if abnormal heart rhythms are happening.
- Echo (echocardiogram) – to look at the movement of blood as it flows through the heart and search for ‘spongy’ areas.
Although LVNC cannot be cured, treatment can control any symptoms caused by a reduction in how well the heart is working as a pump, or by problems with the electrical signalling in the heart. Treatment aims to help to improve the heart's function and to reduce any complications. Treatment is guided by the results of the diagnostic tests and the symptoms, and so is individualised based on the symptoms they are experiencing.
Treatment may include medication, implantable devices, surgery and lifestyle management.
Heart with LVNC