What is Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)?
-
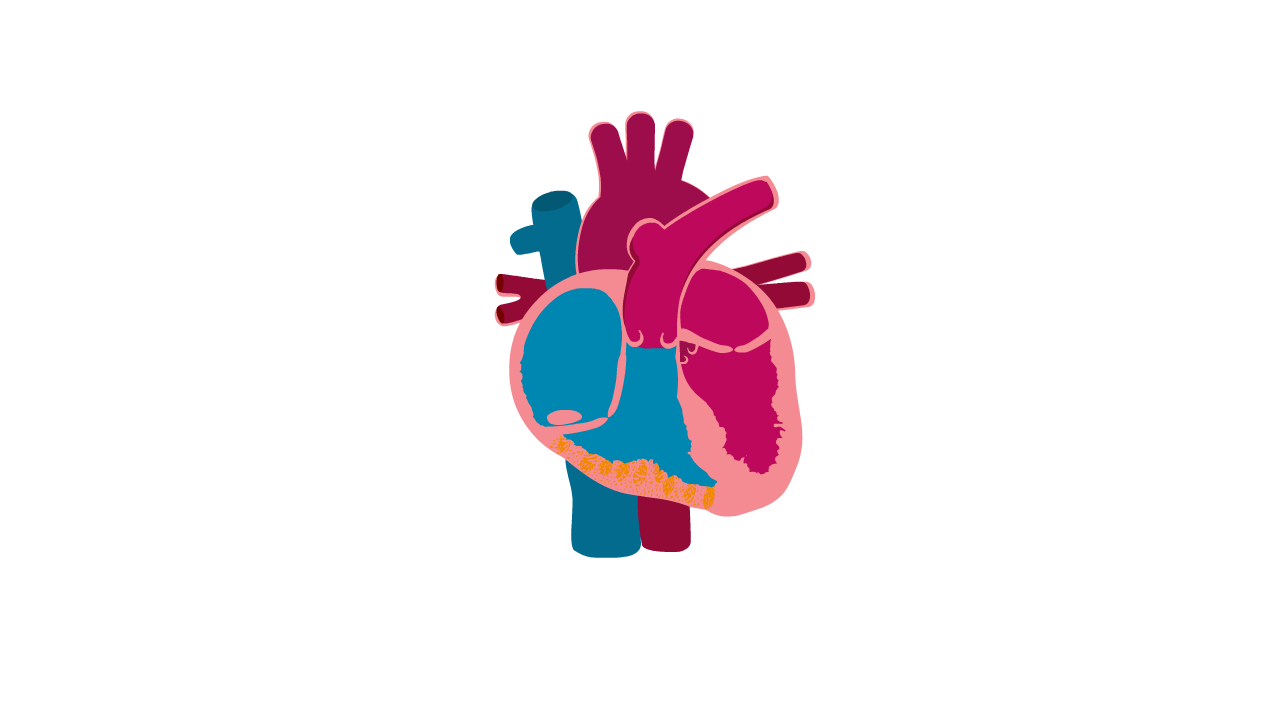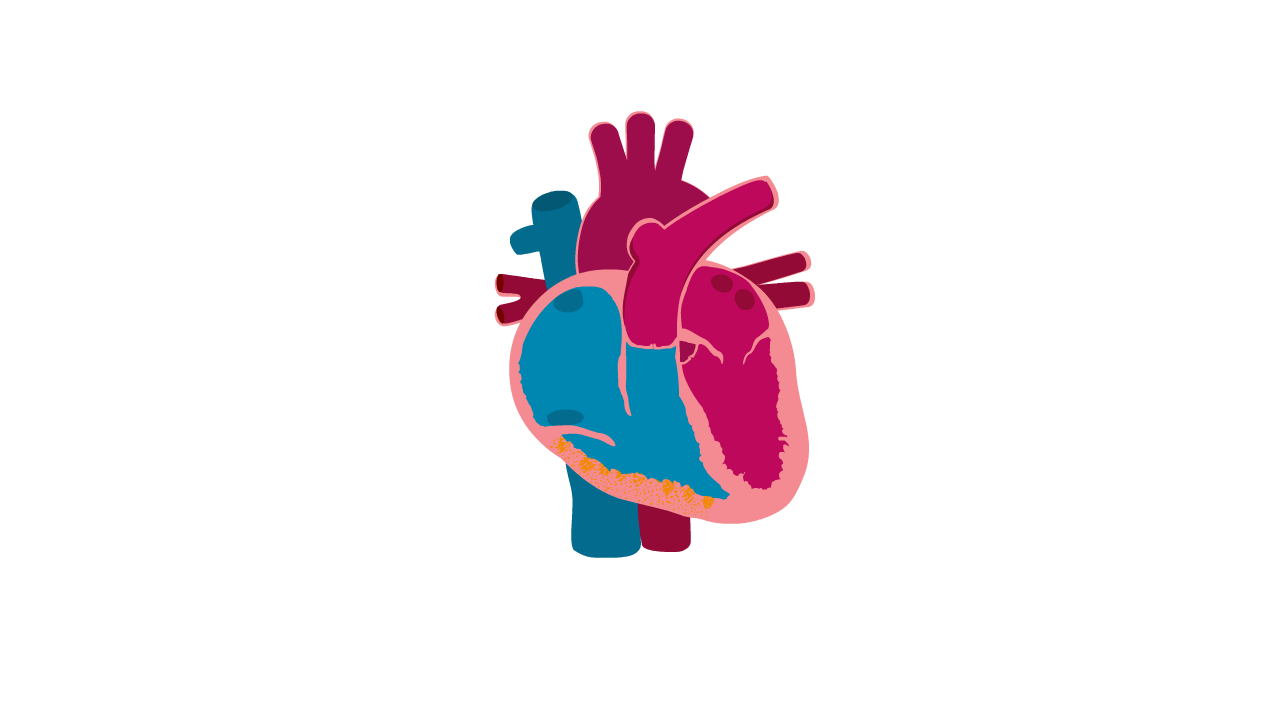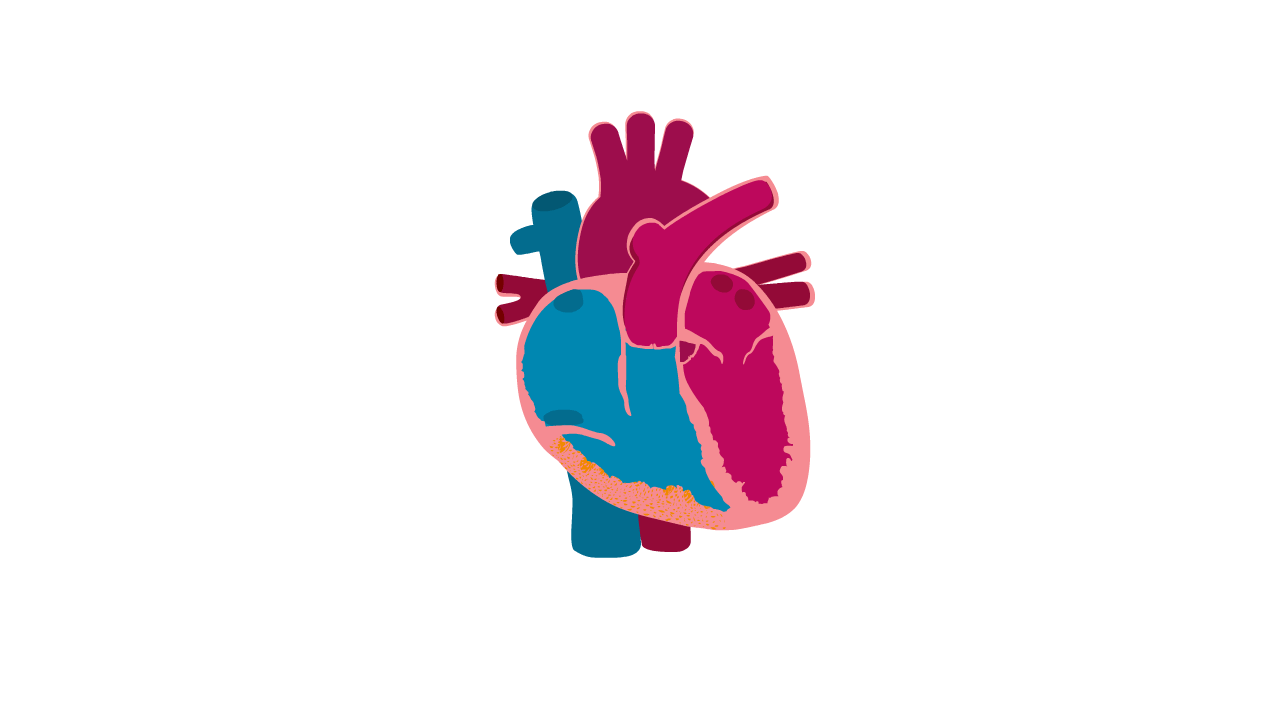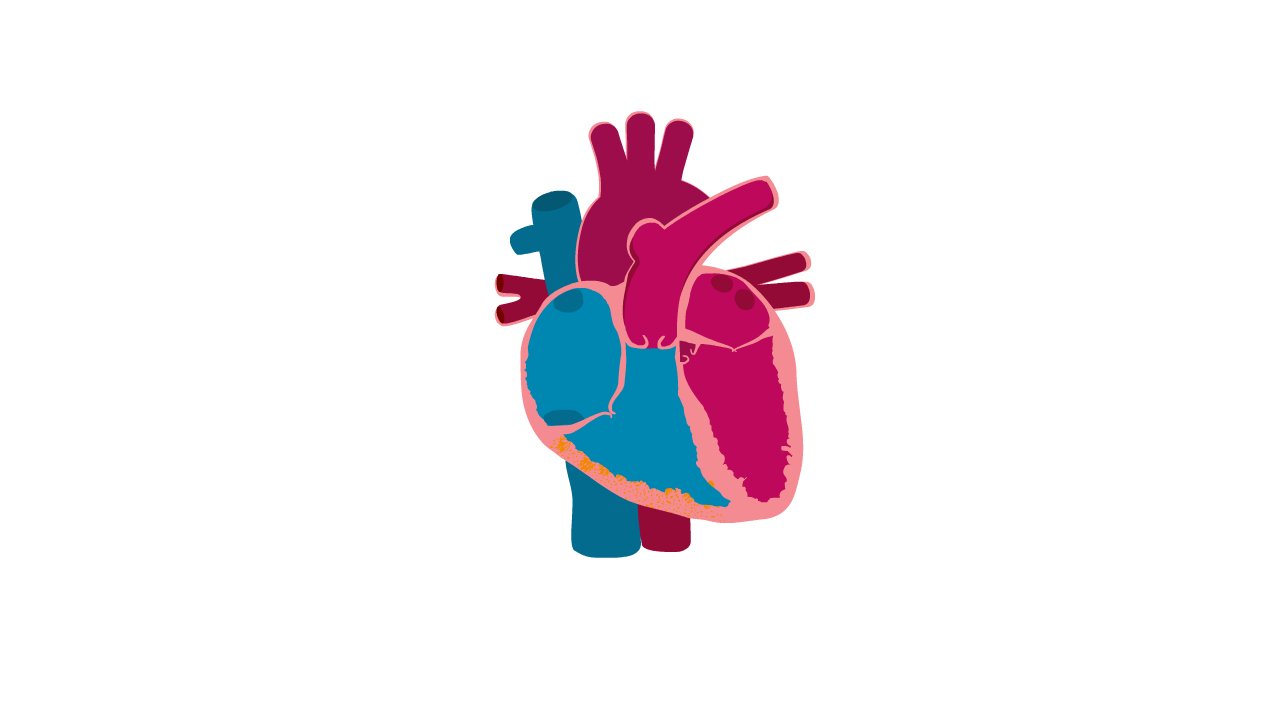
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, or ARVC, is a type of cardiomyopathy that affects the lower pumping chambers of the heart and causes abnormal heart rhythms.
-
ARVC is sometimes called arrhythmic cardiomyopathy as the main symptoms are arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms).
Some of the symptoms are related to the electrical activity of the heart as well as the structure of the heart and how well it pumps.
Symptoms can include the following:
- Palpitations (feeling your heart beating too fast, too hard or like it is ‘fluttering’) – this is caused by abnormal heart rhythms.
- Light-headedness and fainting (loss of consciousness) – reduced oxygen levels or blood flow to the brain can be caused by abnormal heart rhythms.
- Swollen legs, ankles and tummy – as the heart isn’t pumping effectively.
- Breathlessness – as fluid builds up around the lungs.
ARVC can be difficult to diagnose as the changes in the heart can be subtle and the fat deposits can be hard to see. The heart chambers can become enlarged, meaning that it is sometimes misdiagnosed as dilated cardiomyopathy.
- Medical history – to look at symptoms and whether other family members have this condition (as it can be genetic).
- Physical exam – to see what physical symptoms, if any, are happening.
- ECG (electrocardiogram) – this looks at the electrical activity of the heart and whether abnormal heart rhythms are happening.
Although there is no cure for ARVC, treatments are used to reduce and control symptoms, and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment focuses on improving the pumping of the heart and controlling abnormal heart rhythms.
Treatments include medication, implantable devices, surgery and lifestyle management.
Heart with ARVC